The Core Components of a Car's Charging System
26-Jul-2024
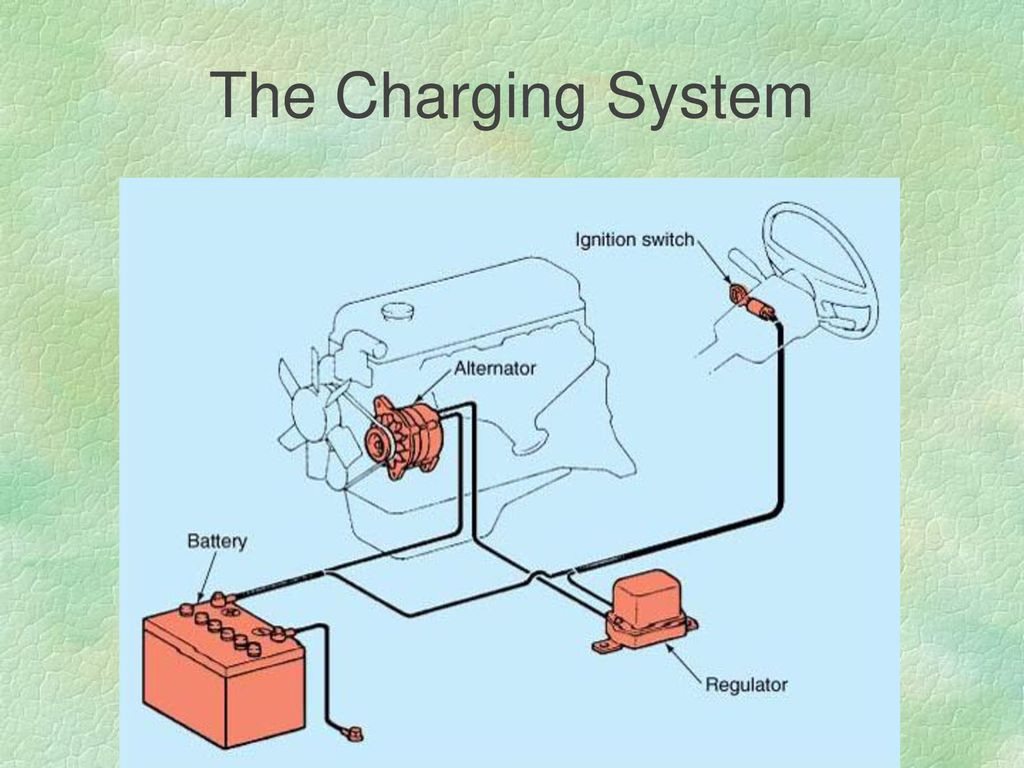
The charging system in a car is responsible for ensuring that the battery is always charged and ready to provide power to the vehicle. It consists of several core components that work together to generate and regulate electrical power. These components include the battery, ignition switch, alternator, and regulator.
The battery is the heart of the charging system. It stores electrical energy and provides power to start the engine and operate the electrical systems when the engine is not running. The ignition switch controls the flow of electrical power from the battery to the rest of the vehicle.
The alternator is a key component of the charging system. It is driven by the engine and generates electricity to recharge the battery and power the electrical systems while the engine is running. The regulator controls the output of the alternator to ensure that the battery is charged at the correct voltage and prevent overcharging.
The Role of the Battery in Vehicle Power Management
It is responsible for providing the initial power to start the engine and for supplying electrical energy to the various systems and components when the engine is not running.
When you turn the key in the ignition, the battery sends a large surge of electrical power to the starter motor, which cranks the engine and initiates combustion. Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over and supplies power to the electrical systems while also replenishing the battery's charge.
In addition to starting the engine, the battery also powers the lights, radio, air conditioning, and other electrical components when the engine is off. It acts as a backup power source, allowing you to use these systems even when the engine is not running.
How the Alternator and Regulator Work Together
The alternator and regulator work together to ensure that the battery is charged at the correct voltage and prevent overcharging.
When the engine is running, the alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. It generates alternating current (AC), which is then converted into direct current (DC) by the rectifier diodes. The DC power is used to recharge the battery and power the electrical systems.
The regulator is responsible for controlling the output of the alternator. It monitors the voltage of the battery and adjusts the field current of the alternator to regulate the charging voltage. If the battery voltage is low, the regulator increases the field current to generate more charging voltage. If the battery voltage is high, the regulator decreases the field current to reduce the charging voltage.
This dynamic regulation ensures that the battery is charged at the optimal voltage, preventing overcharging and prolonging the battery's lifespan.
Common Charging System Issues and Diagnostic Tips
Despite their importance, charging systems can experience issues that affect their performance. Here are some common charging system issues and diagnostic tips to help you troubleshoot:
- Dead Battery: If your battery is completely dead and the engine won't start, it may be a sign of a faulty alternator or a parasitic drain on the battery. Use a multimeter to test the battery voltage and check for any voltage drop when the engine is off.
- Low Charging Voltage: If you notice that your battery is not charging properly or the electrical systems are not functioning correctly, it could be due to a low charging voltage. This can be caused by a faulty alternator or a loose or corroded connection. Check the alternator output voltage and inspect the battery terminals for any signs of corrosion.
- Overcharging: If your battery is constantly being overcharged, it can cause damage to the battery and other electrical components. This can be caused by a faulty regulator or a shorted diode in the alternator. Test the charging voltage and inspect the regulator and diodes for any signs of damage.
Remember, if you are unsure about diagnosing or repairing any charging system issues, it is always best to consult a professional mechanic.
Maintaining Your Car's Charging System for Optimal Performance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your car's charging system, regular maintenance is essential. Here are some tips to help you maintain your charging system:
- Keep the Battery Clean: Regularly inspect the battery terminals and clean them if there is any corrosion. Corroded terminals can prevent proper electrical contact and reduce the charging efficiency.
- Check the Belt Tension: The alternator is driven by a belt connected to the engine. Over time, the belt can become loose or worn, affecting the performance of the alternator. Inspect the belt tension regularly and adjust or replace the belt if necessary.
- Test the Charging System: Periodically test the charging system to ensure that the alternator is generating the correct voltage and the battery is being charged properly. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Try to avoid fully discharging the battery, as it can shorten its lifespan. If you frequently use electrical accessories without the engine running, consider installing a deep-cycle battery that is designed for this type of usage.
By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your car's charging system in top condition and avoid unexpected breakdowns on the road.The Core Components of a Car's Charging System
The charging system in a car is responsible for ensuring that the battery is always charged and ready to provide power to the vehicle. It consists of several core components that work together to generate and regulate electrical power. These components include the battery, ignition switch, alternator, and regulator.
The battery is the heart of the charging system. It stores electrical energy and provides power to start the engine and operate the electrical systems when the engine is not running. The ignition switch controls the flow of electrical power from the battery to the rest of the vehicle.
The alternator is a key component of the charging system. It is driven by the engine and generates electricity to recharge the battery and power the electrical systems while the engine is running. The regulator controls the output of the alternator to ensure that the battery is charged at the correct voltage and prevent overcharging.
The Role of the Battery in Vehicle Power Management
It is responsible for providing the initial power to start the engine and for supplying electrical energy to the various systems and components when the engine is not running.
When you turn the key in the ignition, the battery sends a large surge of electrical power to the starter motor, which cranks the engine and initiates combustion. Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over and supplies power to the electrical systems while also replenishing the battery's charge.
In addition to starting the engine, the battery also powers the lights, radio, air conditioning, and other electrical components when the engine is off. It acts as a backup power source, allowing you to use these systems even when the engine is not running.
How the Alternator and Regulator Work Together
The alternator and regulator work together to ensure that the battery is charged at the correct voltage and prevent overcharging.
When the engine is running, the alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. It generates alternating current (AC), which is then converted into direct current (DC) by the rectifier diodes. The DC power is used to recharge the battery and power the electrical systems.
The regulator is responsible for controlling the output of the alternator. It monitors the voltage of the battery and adjusts the field current of the alternator to regulate the charging voltage. If the battery voltage is low, the regulator increases the field current to generate more charging voltage. If the battery voltage is high, the regulator decreases the field current to reduce the charging voltage.
This dynamic regulation ensures that the battery is charged at the optimal voltage, preventing overcharging and prolonging the battery's lifespan.
Common Charging System Issues and Diagnostic Tips
Despite their importance, charging systems can experience issues that affect their performance. Here are some common charging system issues and diagnostic tips to help you troubleshoot:
- Dead Battery: If your battery is completely dead and the engine won't start, it may be a sign of a faulty alternator or a parasitic drain on the battery. Use a multimeter to test the battery voltage and check for any voltage drop when the engine is off.
- Low Charging Voltage: If you notice that your battery is not charging properly or the electrical systems are not functioning correctly, it could be due to a low charging voltage. This can be caused by a faulty alternator or a loose or corroded connection. Check the alternator output voltage and inspect the battery terminals for any signs of corrosion.
- Overcharging: If your battery is constantly being overcharged, it can cause damage to the battery and other electrical components. This can be caused by a faulty regulator or a shorted diode in the alternator. Test the charging voltage and inspect the regulator and diodes for any signs of damage.
Remember, if you are unsure about diagnosing or repairing any charging system issues, it is always best to consult a professional mechanic.
Maintaining Your Car's Charging System for Optimal Performance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your car's charging system, regular maintenance is essential. Here are some tips to help you maintain your charging system:
- Keep the Battery Clean: Regularly inspect the battery terminals and clean them if there is any corrosion. Corroded terminals can prevent proper electrical contact and reduce the charging efficiency.
- Check the Belt Tension: The alternator is driven by a belt connected to the engine. Over time, the belt can become loose or worn, affecting the performance of the alternator. Inspect the belt tension regularly and adjust or replace the belt if necessary.
- Test the Charging System: Periodically test the charging system to ensure that the alternator is generating the correct voltage and the battery is being charged properly. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Try to avoid fully discharging the battery, as it can shorten its lifespan. If you frequently use electrical accessories without the engine running, consider installing a deep-cycle battery that is designed for this type of usage.
By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your car's charging system in top condition and avoid unexpected breakdowns on the road.

 Loading..
Loading..