How Brake Drums Function: Understanding This Vital Component of Your Vehicle’s Braking System
Brake drums are a critical component in many vehicles' braking systems, especially in older cars, trucks, and some heavy-duty vehicles. While modern cars mostly use disc brakes, brake drums remain an effective and reliable braking solution for certain applications. In this article, we’ll dive into how brake drums function, how they differ from other types of brakes, and why they’re important for your vehicle’s safety.
What Are Brake Drums?
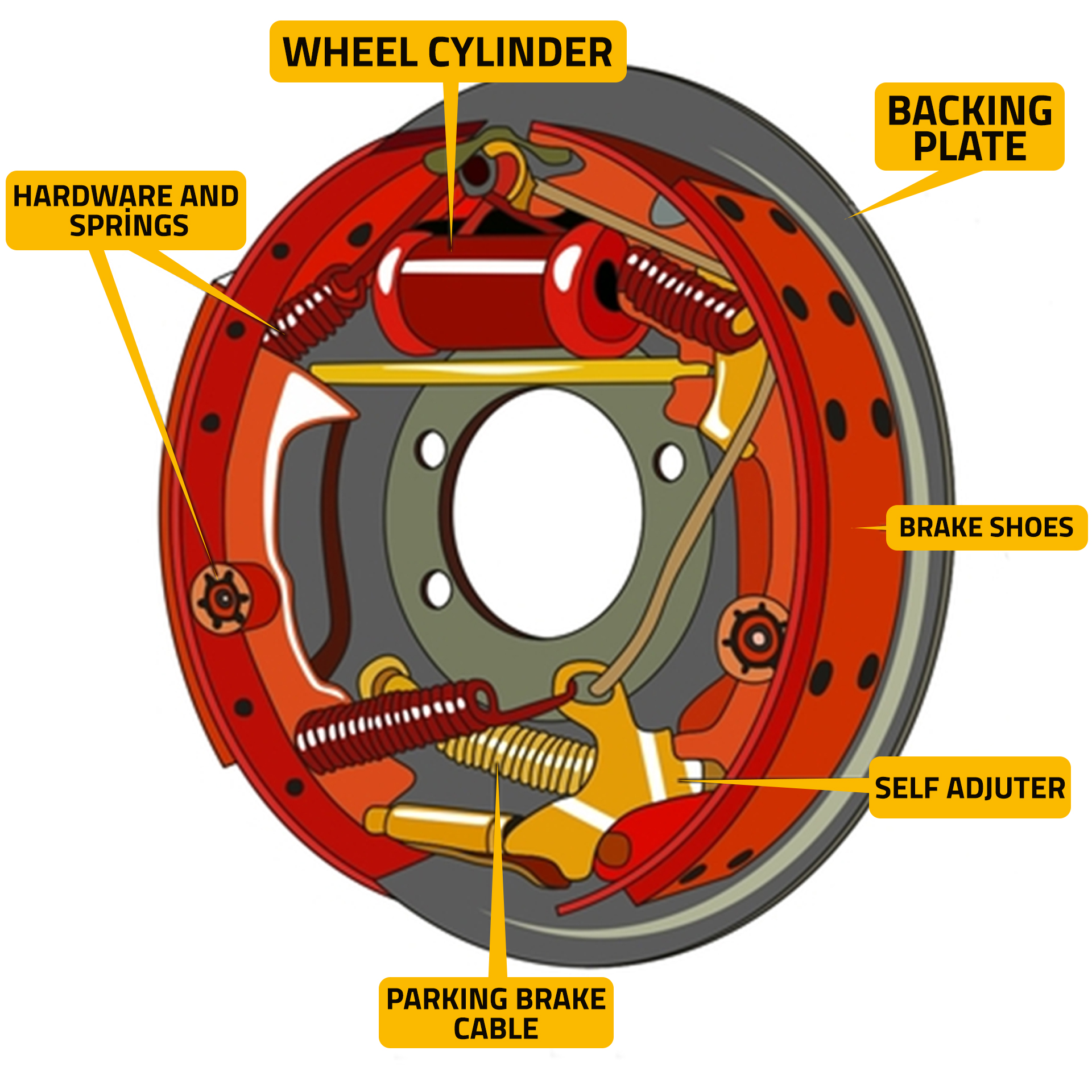
Brake drums are cylindrical components attached to the wheel hub and are commonly found in rear-wheel drive vehicles. Unlike disc brakes that use calipers to clamp onto a rotor, drum brakes rely on friction created by brake shoes pressing against the inner surface of the drum. This friction slows down the vehicle and eventually brings it to a stop.
How Do Brake Drums Work?
When you press the brake pedal, the following sequence occurs in a drum braking system:
- Brake Fluid Activation: Pressing the brake pedal pushes brake fluid through the brake lines, creating hydraulic pressure.
- Wheel Cylinder Activation: The hydraulic pressure activates a wheel cylinder inside the drum.
- Brake Shoes Expand: The wheel cylinder forces two brake shoes apart, pressing them against the inside surface of the rotating drum.
- Friction and Heat: The contact between the brake shoes and the drum generates friction, slowing down the wheel and ultimately the vehicle.
- Release Mechanism: When you release the brake pedal, springs within the drum retract the brake shoes, allowing the drum to rotate freely again.
The friction created during this process is what ultimately brings the vehicle to a stop. Because brake drums rely on hydraulic pressure, they are highly effective and provide the necessary stopping power, especially in lower-speed, heavy-duty applications.
Key Components of Brake Drums
A brake drum system is made up of several important parts that work together to ensure smooth and effective braking:
- Brake Drum: The drum itself is attached to the wheel hub and rotates with the wheel.
- Brake Shoes: These are metal plates lined with a friction material (similar to brake pads) that press against the drum to create friction.
- Wheel Cylinder: The wheel cylinder uses hydraulic pressure to push the brake shoes against the drum.
- Return Springs: These springs pull the brake shoes back to their original position once you release the brake pedal.
Each part plays a critical role in ensuring that the brake drum functions properly. Regular maintenance is essential to keep these components in top condition, as worn parts can lead to decreased braking performance and potentially unsafe driving conditions.
Advantages of Brake Drums
While disc brakes are more common today, brake drums have specific advantages that make them suitable for certain vehicles:
- Durability: Brake drums are generally long-lasting and can endure high levels of stress, making them ideal for trucks and larger vehicles.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Drum brakes are often more affordable than disc brakes, both in terms of initial cost and maintenance.
- Better for Parking Brakes: Brake drums are often integrated with the parking brake, making them effective in providing secure stops when the vehicle is stationary.
- Higher Friction: Drum brakes can create more friction, which is beneficial in heavy-duty applications that require strong stopping power.
Signs Your Brake Drums May Need Attention
To maintain safe braking performance, it’s crucial to recognize signs of worn brake drums. Here are some common indicators that your brake drums or brake shoes may need inspection or replacement:
- Vibrations or Pulsing: If you feel a pulsing sensation in the brake pedal, it could mean your brake drum is warped or worn unevenly.
- Reduced Braking Power: If your vehicle takes longer to stop, it may be due to worn brake shoes or a damaged drum.
- Squeaking or Grinding Sounds: A squeak when braking might indicate that the friction material on the brake shoes is worn down.
- Parking Brake Issues: Since drum brakes often serve as the parking brake, difficulty holding the car in place on a hill can suggest issues with the drum brake system.
Regular Maintenance for Brake Drums
To ensure optimal performance, brake drum maintenance is essential. Here are a few maintenance tips to keep your drum brakes functioning effectively:
- Inspect Brake Shoes Regularly: Brake shoes wear down over time and should be checked regularly to ensure they have sufficient friction material.
- Clean the Brake Drum Surface: Dust and debris can build up inside the drum, so it’s important to clean them periodically.
- Replace Worn Parts: If any component, such as the brake shoes or springs, shows significant wear, replace them promptly to maintain safe braking.
Maintaining your brake drum system ensures reliable stopping power and a safer driving experience. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent costly repairs and avoid unsafe situations on the road.
Why Understanding Brake Drums is Important
Whether you drive a vehicle with drum brakes or disc brakes, understanding how each braking system works helps you make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs. Drum brakes are a tried-and-true technology that, when well-maintained, offer reliable and powerful braking. For vehicle owners, keeping an eye out for the signs of wear and scheduling regular check-ups can go a long way toward ensuring your safety.
Final Thoughts
Brake drums may be older technology, but they continue to play a crucial role in vehicle safety, especially in heavy-duty and rear-wheel drive vehicles. Understanding how brake drums function allows drivers to identify issues early and maintain safe braking performance. If you’re looking to replace or upgrade your brake drums, consult a trusted professional or retailer to find the best options for your vehicle.

 Loading..
Loading..