Gasoline vs Electric Vehicles: A Detailed Comparison
Explore the future of driving: Are electric vehicles really set to overtake their gasoline-powered counterparts?
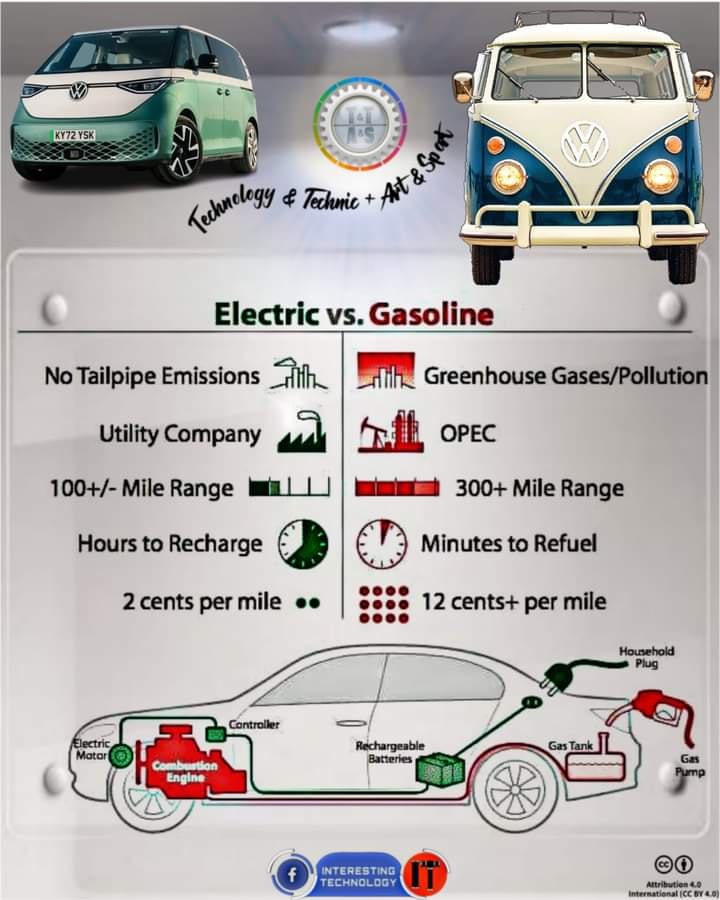
Understanding the Basics: How Gasoline and Electric Vehicles Work
Gasoline vehicles rely on internal combustion engines to convert fuel into mechanical energy, which powers the vehicle. These engines burn gasoline or diesel fuel, producing exhaust gases that are emitted into the atmosphere.
Electric vehicles, on the other hand, are powered by electric motors that run on electricity stored in batteries. When the vehicle is in motion, the electric motor converts the stored energy into mechanical energy, propelling the vehicle forward. This means that electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them more environmentally friendly.
Both gasoline and electric vehicles have their own advantages and disadvantages when it comes to how they work. Understanding these basics is crucial in comparing the two.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sustainability
One of the key differences between gasoline and electric vehicles is their environmental impact.
Gasoline vehicles emit various pollutants, including carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM), which contribute to air pollution and climate change. Additionally, gasoline vehicles rely on fossil fuels, which are finite resources and contribute to carbon emissions throughout the production and refining process.
On the other hand, electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. However, the environmental impact of electric vehicles largely depends on how the electricity used to charge them is generated. If the electricity comes from renewable sources, such as solar or wind power, the environmental benefits are even greater.
In terms of sustainability, electric vehicles have the potential to be more sustainable than gasoline vehicles. As technology improves and renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the environmental impact of electric vehicles is expected to decrease even further.
Long-term Costs: Maintenance and Fuel Efficiency
When it comes to long-term costs, there are several factors to consider for both gasoline and electric vehicles.
In terms of maintenance, gasoline vehicles generally require more frequent and expensive maintenance compared to electric vehicles. Gasoline engines have more moving parts and fluids that need regular servicing, such as oil changes and spark plug replacements. Electric vehicles, on the other hand, have fewer moving parts and do not require oil changes. They also have regenerative braking systems, which reduce wear on brake pads.
Fuel efficiency is another important factor to consider. Electric vehicles are generally more energy-efficient than gasoline vehicles. They can convert a higher percentage of the energy stored in their batteries into mechanical energy, resulting in lower energy consumption and lower fuel costs. Additionally, the cost of electricity is often cheaper than gasoline, further reducing the overall cost of ownership.
However, it's important to note that the upfront cost of electric vehicles is typically higher than gasoline vehicles. This is mainly due to the cost of the battery, which is the most expensive component of an electric vehicle. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, the cost of electric vehicles is expected to decrease.
Performance and Technology: Speed, Handling, and Innovations
When it comes to performance, both gasoline and electric vehicles have their own strengths.
Gasoline vehicles are known for their high horsepower and torque, providing quick acceleration and higher top speeds. They also have a longer driving range and can be refueled quickly at gas stations.
On the other hand, electric vehicles are known for their instant torque, delivering quick acceleration from a standstill. They also have a lower center of gravity due to the placement of heavy batteries, which improves handling and stability. Electric vehicles also have the advantage of regenerative braking, which converts kinetic energy into electrical energy, further improving efficiency and range.
In terms of technology, electric vehicles are at the forefront of innovation. They often come with advanced features such as regenerative braking, energy-saving modes, and smart charging capabilities. Additionally, electric vehicle technology is rapidly evolving, with improvements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and range. This makes electric vehicles an exciting choice for those interested in cutting-edge technology.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences: What's Driving the Shift?
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant shift towards electric vehicles, driven by several factors.
One of the main driving forces is the increasing concern over climate change and air pollution. Governments around the world are implementing stricter emissions regulations, incentivizing the adoption of electric vehicles through subsidies and tax benefits. Consumers are also becoming more environmentally conscious and are actively seeking greener transportation options.
Another factor driving the shift towards electric vehicles is the advancement of technology. Battery technology has improved significantly in recent years, allowing for longer range and faster charging times. Additionally, the development of charging infrastructure is making electric vehicles more practical and convenient for everyday use.
Furthermore, the cost of owning and operating electric vehicles is becoming more competitive with gasoline vehicles. The decreasing cost of batteries, along with the potential for lower maintenance and fuel costs, makes electric vehicles an attractive option for cost-conscious consumers.
Overall, the market trends and consumer preferences indicate a promising future for electric vehicles. As technology continues to advance and infrastructure improves, electric vehicles are expected to become the norm rather than the exception in the automotive industry.

 Loading..
Loading..